
You can see LED displays in many places, like billboards and meeting rooms. Manufacturers make these screens by following the LED Display Manufacturing Process. This process starts with picking the best materials. Every step, like putting parts together, testing, and checking quality, affects how long the display works and how clear the picture is. Manufacturers use new methods, such as micro-pitch and transparent LED technology, to make screens brighter and more dependable. The LED display market around the world keeps getting bigger, as you can see below:
Picking good materials like aluminum and silicone makes LED displays last longer. These materials also help the displays work well in hard places. Careful checking and testing at each step finds problems early. This makes sure the display is safe and bright. Using new ways like SMT and reflow soldering makes the work more exact. These methods also help make high-resolution screens faster. Putting LEDs in the right way with the best tools stops mistakes. Good planning keeps the screen clear and strong. Strong frames, special coatings, and good packaging keep the display safe from weather and harm. This helps the display last longer.
To build an LED display, you must pick the right materials. Good materials help your screen work well and last longer. Each part is chosen for what it can do:
l Aluminum Alloy: This is used in LED strip housings. It moves heat away, is light but strong, and does not rust. This metal helps the display stay cool and last longer.
l Polycarbonate (PC) Plastic: This is found in diffusers and covers. It is tough, clear, and blocks UV rays. It keeps your display safe and easy to see.
l Silicone Rubber: This material is bendy and keeps water out. It also stands up to chemicals. It works well for displays outside or in factories because it can handle hot and cold.
l Copper-Clad Flexible PCB (FPCB): This is the base for the LED strip. It lets electricity flow well and spreads out heat. It is also bendy and does not break easily.
Tip: If you use good materials, your LED display will work well in tough places and last a long time.
You also need to think about the semiconductor compounds that make the light. Here are some common ones:
Compound | Main Use | Color Produced |
InGaN | LED chips | Blue, Ultraviolet |
GaN | LED chips | Blue, Green |
GaP | LED chips | Green, Red |
AlGaInP | LED chips | Red, Orange |
GaAsP | LED chips | Red, Infrared |
GaAlAs | LED chips | Infrared |
These compounds help your LED display show bright and bold colors.
You have to follow strict rules when picking and checking LED display parts. Some rules are IEC 60598 for safety, IES LM-80 for light, ENERGY STAR for saving power, and UL Certification for North America. Following these rules keeps your display safe and working well.
Before putting the display together, check every part:
Make sure power cables are connected right (red to positive, black to negative) so it works safely.
Check data cables to be sure the modules talk to each other.
Look at each board for bends, good solder, and correct parts.
Use Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) to find missing or wrong parts.
Use X-ray inspection to look for hidden solder problems, especially in tricky chips.
Do In-Circuit Testing (ICT) to check electric values and if parts are in the right place.
Note: Careful checks now stop problems later and help your LED display work its best.
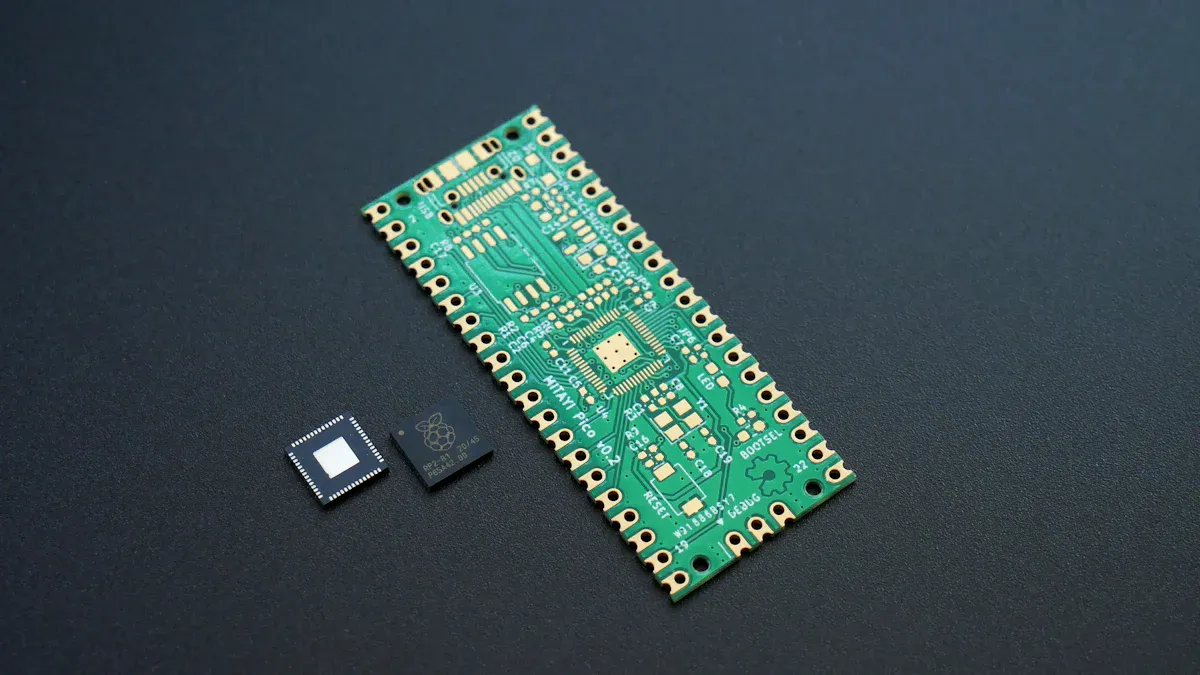
The LED Display Manufacturing Process starts with making the printed circuit board, or PCB. The PCB is like the main support for your display. Most LED displays use aluminum PCBs because they help move heat away from the LEDs. These boards have three layers. There is a base aluminum layer, a thermal insulation layer, and a copper circuit layer. You can pick from flexible aluminum, hybrid aluminum, or multilayer aluminum boards. Flexible aluminum lets you bend the board one time. This helps you use fewer connectors. Hybrid aluminum mixes aluminum with FR-4. This makes the board strong and costs less. Multilayer aluminum gives better heat control for displays that need high performance.
Before adding parts, you must finish the board. This means putting on a surface finish like gold or silver. You also print important markings and test the board with special machines. The board is cut to the right shape. Good planning and careful wiring help your display stay safe and last longer.
Surface-mount technology, or SMT, lets machines put tiny LED parts on the board. This step is fast and very accurate. SMT helps you fit more parts on each board. This is important for high-resolution displays. Pick-and-place robots put each part in the right spot. Solder paste stencils add solder only where it is needed. Automated optical inspection checks if every part is in the right place. It also checks if each solder joint looks good. SMT lowers mistakes, saves money, and helps you make many boards quickly.
After placing the parts, you use reflow soldering to attach them. The board goes through an oven with different heat zones. First, the board heats up slowly. Then, it stays at a set temperature for a while. Next, it gets hotter, reaching between 235째C and 250째C. This melts the solder and connects the parts. Cooling happens at about 2 to 4째C per second. This keeps the joints strong. For small-pitch displays, you must control the heat carefully to protect the LEDs. You can use thermocouples to check the heat at important spots. Baking the LED lamps before soldering removes moisture. This keeps the LEDs stable during the process.
Tip: If you control the heat and bake the parts, you can stop defects and help your LED display last a long time.
Mounting LEDs is a big part of the LED Display Manufacturing Process. This step affects how clear and strong your screen will be. There are three main ways to mount LEDs: SMD, COB, and MicroLED. Each way has its own good points and best uses.
Feature | SMD (Surface Mounted Device) | COB (Chip on Board) |
Packaging Method | Single LED chips are soldered onto the PCB | Many LED chips are put right on the PCB and covered |
Light Source Type | Makes light from one point | Makes light from a bigger area |
Pixel Pitch Support | Works for P1.25 and higher | Can go as small as P0.4 |
Display Effect | May look blocky if you stand close | Light looks soft and colors are bright |
Heat Dissipation | Okay, but heat travels farther | Good, heat moves out fast |
Durability | Not as strong | Strong, keeps out water and dust |
Maintenance Cost | Cheaper and easier to fix | Costs more and is harder to fix |
Production Cost | Cheaper, easy to make | Costs more, harder to make |
Application | Good for big, cheaper screens | Best for fancy, close-up screens |
MicroLED is a newer way in the LED Display Manufacturing Process. It uses mass transfer to put tiny LED chips on the base. This makes the screen very bright and lets you use very small pixels. MicroLED screens use film to cover the parts. This makes them thin, light, and tough.
You need special tools to mount LEDs. Laser tools help you put each LED in the right spot. This is very important for small-pitch and see-through screens. Some new ways, like flip-chip COB, help move heat out and make the screen last longer.
You might have some problems when mounting:
l Taking out old parts without breaking them
l Reaching hard spots
l Wires that do not fit new LEDs
l Problems with dimming or controls
l Not knowing how many parts you need
l Forgetting about changes in power needs
l Drivers that stop working or lights that blink
l Problems from other electronics nearby
l Too much heat from bad setup
l Bad wiring or loose wires
To fix these problems, you should:
l Teach your team and use the right tools
l Plan well and check everything first
l Use easy-to-change wires and check if things fit
l Update systems if needed
l Hire skilled workers and follow safety steps
l Pick good products and check wires often
Tip: Careful work and good planning help you stop mistakes and keep your LED display working well.
After you put in the LEDs, you must test them. This makes sure they work right. This part of the LED Display Manufacturing Process checks the light, color, and if the LEDs are steady.
You do these steps:
l Luminous Flux Measurement: Use a special ball to see how much light comes out. This tells you how bright the screen is.
l Light Intensity Testing: Use tools to check how strong and where the light goes. This helps you find weak or uneven spots.
l Spectral Parameter Testing: Use prisms or gratings to check the color and quality of the light. This makes sure the colors look real and bright.
l Switching Characteristics Testing: Turn the LEDs on and off to see how fast and smooth they work. This checks for blinking or color changes.
If you find problems, you can fix them before moving on. Careful testing keeps the LED Display Manufacturing Process going well and gives you a great screen.
You need to frame each LED module to make your screen strong. Module framing holds the modules and keeps them lined up. This step is key for a smooth picture and a screen that lasts.
l The frame keeps the modules in place and flat. This stops gaps or bumpy spots.
l Cabinet screens use metal or plastic frames with locks and holes. These help you line up the modules just right.
l The frame keeps dust, water, and electric problems away from the inside parts.
l Steel or aluminum frames hold up heavy screens and stand up to wind. This is important for big or outdoor screens.
l The frame also makes it easy to change or fix modules.
Note: A strong frame keeps your LED display safe and looking good, even outside.
The last step here in the LED Display Manufacturing Process is putting on three anti-paint. This special paint keeps water, dust, and rust away from your LED modules. You put it on the back of outdoor modules. With silica gel on the front and waterproof covers, this paint helps your screen get an IP65 rating. That means it can handle rain, dust, and bad weather.
The three anti-paint works with other layers to seal the module. This keeps your screen working well for a long time, even outside or in factories.
Tip: Always use three anti-paint for outdoor screens. It keeps your screen safe and working for many years.
Every LED display must be checked before leaving the factory. First, look at all hardware connections like power cords and signal cables. Also check the mounting brackets. Turn on the display and watch for flickering or black screens. Look for any strange colors too. Change the brightness and contrast to fit the room. Use special tools to make sure the colors match everywhere. Run the display for many hours or days. Watch for changes in brightness, color, or heat. This helps you find problems early and fix them. It makes sure your display works well.
Tip: Write down each debugging step and report problems. This helps you do better next time and keeps defects low.
You need to test if your LED display can handle tough places. Put the display in hot and cold rooms from -20째C to 50째C. Test it in wet air from 10% to 90% humidity. Use tests for salt spray, sand, dust, shaking, and dropping. The table below shows some common tests:
Environmental Test | Purpose |
High/Low Temperature | Checks performance in extreme heat or cold |
Humidity Cycle | Tests resistance to moisture |
Salt Spray | Measures corrosion resistance |
Sand and Dust | Checks protection from particles |
Vibration/Impact/Drop | Tests strength during transport or use |
ESD (Electrostatic) | Prevents damage from static electricity |
These tests help stop problems from weather, shipping, or rough handling.
Pick the right cabinet material for your display. The cabinet keeps inside parts safe and helps with heat and weight. Here is a quick comparison:
Material | Pros | Cons |
Iron/Steel | Strong, low cost | Heavy, can rust |
Die-Cast Aluminum | Light, precise, resists corrosion | Higher cost, dents easily |
Magnesium Alloy | Very light, strong, good heat control | Expensive, less rugged |
Carbon Fiber | Extremely light, strong | Very expensive |
Use screws to hold all modules tight. Make sure the case fits well. This keeps out dust, water, and shocks.
Good packaging keeps your LED display safe when shipping. Use wooden boxes with foam and anti-static bags. Add packets to keep out water. Make corners strong and put labels on each box. For shipping far away, use steel belt wooden boxes. These are strong and easy to move. Always check the boxes and displays when they arrive. Store them in a dry, clean place until you set them up.
Note: Careful packaging and clear labels stop damage and help you install the display faster and safer.
You can be sure each step in making an LED display keeps your display safe. Picking good materials and testing at the end helps protect your money. Controlling things like heat and checking settings makes the display last longer. It also saves power. Careful work and following rules make the screen brighter and colors better. It also keeps the display safe to use. When you buy a display, check for signs of good quality at every step.
You must focus on quality control. This step checks every part and process. It helps you catch problems early. Good quality control ensures your display works well and lasts longer.
You use materials like aluminum for heat dissipation. You also design the PCB to spread heat. Proper airflow in the cabinet helps. These steps keep your display cool and stable.
Yes, you can repair most modules. You remove the faulty part and replace it with a new one. Skilled technicians use special tools for this job. Always test the module after repair.
Look for certifications like UL, CE, and RoHS. These show your display meets safety and environmental standards. Certified displays give you better reliability and peace of mind.