
LCD displays have changed how we use devices like phones and TVs. They work using smart engineering and special materials. In 2023, the worldwide TFT LCD displays market was worth $179.9 billion. It is expected to grow by 3.98% every year until 2033. This growth shows LCD displays are still important, even with new tech coming out. Improvements like faster screen updates and mini-LEDs make them popular in cars and gadgets.
l LCD screens use liquid crystals and lights to show pictures. They don’t make their own light.
l Color LCDs use red, green, and blue dots to show bright pictures. These are perfect for phones and tablets.
l Black-and-white LCDs save energy and work well in sunlight. They are great for calculators and medical tools.
l The LCD driver decides how each dot shows color and light. It sends signals to make pictures clear.
l Backlights are important for seeing the screen. Brighter screens are easier to see in sunlight.
To understand LCD displays, you need to know their main parts. Each part has a job to help create the pictures on your screen. Let’s break them down.
The LCD glass controls how much light passes through to form images. It doesn’t make its own light but uses a backlight to shine through. The glass has layers of polarizers and liquid crystals. These layers work together to block or let light through based on electric signals. This is how the screen becomes visible to you.
Manufacturers test the LCD glass to ensure it works well. Here are some examples:
Test Type | What It Checks |
Storage Temperature Testing | Checks if it can handle hot or cold when turned off. |
Operating Temperature Testing | Tests how it works under voltage in normal temperature ranges. |
Temperature Cycling Testing | Measures how it handles sudden temperature changes. |
Vibration Testing | Tests how it reacts to shaking in different directions. |
Moisture Resistance Testing | Checks if it works in hot and humid conditions. |
Packaging Drop Testing | Ensures the product and box stay intact after being dropped. |
ESD Testing | Tests if it can handle sudden electrical shocks. |
These tests make sure the LCD glass can handle tough conditions.
Liquid crystals are the key material in LCD displays. They flow like a liquid but have molecules that line up like a solid. This lets them control light when electricity is applied.
Each pixel in an LCD has liquid crystals. A pixel is the smallest part of a screen that shows light or color. In color screens, each pixel has three sub-pixels: red, green, and blue. By changing the light in these sub-pixels, the screen makes the colors you see.
Electricity is important for how LCD displays work. When you use your device, electric signals go to the liquid crystals. These signals change how the crystals line up, which controls the light.
For example, when no electricity is sent, the crystals block light, making the pixel dark. When electricity is sent, the crystals let light through, making the pixel bright. This control of light and dark creates the pictures and words on your screen.
Choosing between color TFT LCDs and monochrome LCDs depends on your needs. Each type has special features and uses.
Color TFT LCDs use a smart pixel design to show bright images. Each pixel has three sub-pixels: red, green, and blue (RGB). These sub-pixels mix light to create millions of colors. A tiny switch, called a transistor, controls each sub-pixel. Once the sub-pixel is charged, a small storage unit holds the charge. This keeps the image steady until the screen refreshes.
Here’s a simple look at the pixel setup in color TFT LCDs:
Aspect | Description |
Pixel Structure | Pixels have three sub-pixels: red, green, and blue (RGB). |
Color Depth | 24-bit color depth shows 16.7 million colors. |
Refresh Rate | Usually 60Hz for smooth image changes. |
Response Time | Transistors control sub-pixels to reduce motion blur. |
This design helps color TFT LCDs show clear and detailed pictures.
Color TFT LCDs have many benefits for modern devices. They show bright colors and sharp details, improving how things look. High resolutions make even tiny details easy to see. Wide viewing angles, often over 160°, keep the image clear from different positions. New tech like TDDI combines touch and display functions into one chip. This makes devices more reliable and cheaper to produce.
Here are some key features of color TFT LCDs:
Metric | Description |
Resolution | High resolution makes images sharp and detailed. |
Viewing Angles | At least 160° for clear views from any angle. |
Contrast Ratio | Shows the difference between bright and dark areas. |
Brightness | Helps visibility in different lighting. |
Refresh Rates | Faster rates reduce blur and improve motion clarity. |
These features make color TFT LCDs great for phones, tablets, and car screens.
Monochrome LCDs are best for simple, durable, and low-power uses. They use liquid crystals to control light, creating clear images. This makes them perfect for medical tools where details matter. For example, doctors use them to check X-rays because they show excellent contrast.
Common uses for monochrome LCDs include:
l Medical tools like glucose monitors and X-ray systems.
l Industrial machines needing tough, long-lasting screens.
l Everyday gadgets like calculators and e-readers.
Monochrome LCDs beat color TFT LCDs in some ways. They use less power, making batteries last longer. They are easier to see in sunlight, which is great for outdoor use.
Here’s a comparison of key factors between monochrome LCDs and color TFT LCDs:
Factor | Monochrome LCD | Color TFT |
Contrast Ratio | 1:15 (very good) | 1:800 (varies) |
Viewing Angle | 6 o’clock standard | 170°+ (IPS) |
Sunlight Readability | Better (no color fading) | Needs high brightness |
Power Use (Typical) | 150mW | 800mW |
Impact on Battery Life | 30+ days (glucose monitor) | 5-7 days (same battery) |
Unit Price | 15−50 | 50−300+ |
Driver Complexity | Simple | Needs TFT controller |
Lifespan Cost | Lower (100K+ hours) | Higher (50K-80K hours) |
Monochrome LCDs are a top choice when durability and efficiency are key.
The LCD driver works like the brain of the screen. It makes sure each pixel gets the right signal to show clear images. It changes input data into electrical signals to control liquid crystals. Without it, the screen wouldn’t show pictures correctly.
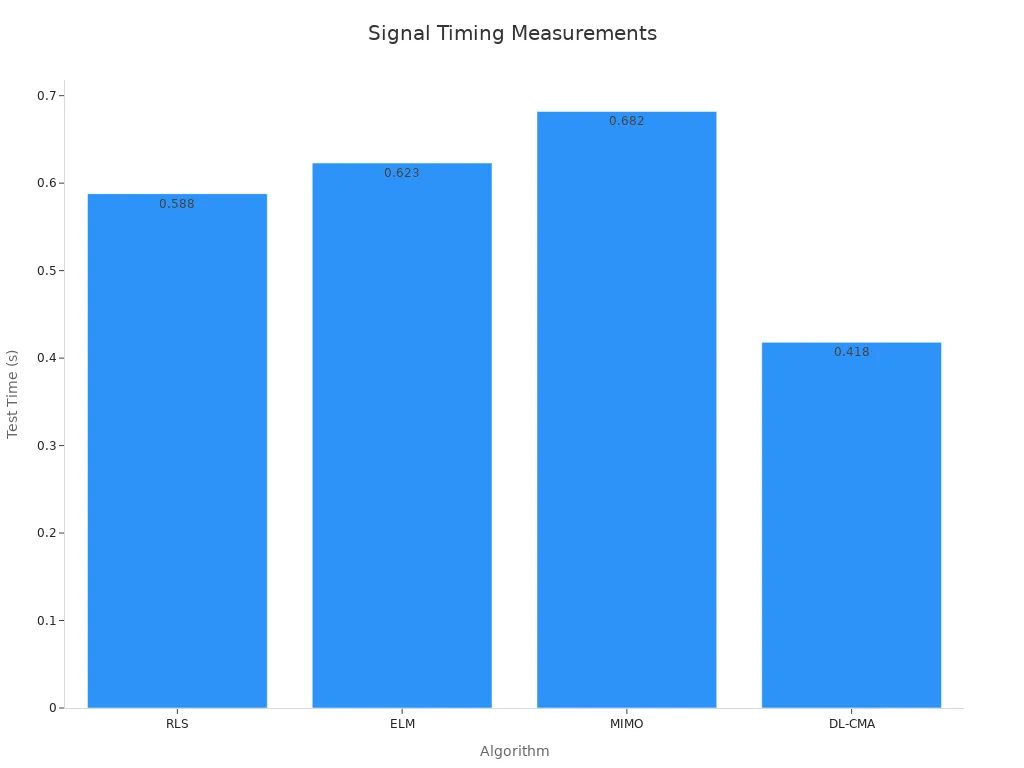
The driver sends signals to pixels to set brightness and color. It uses smart algorithms to work quickly and accurately. For example, the DL-CMA algorithm sends signals in just 0.418 seconds. This is faster than others like MIMO and ELM.
Algorithm | Test Time (s) |
RLS | 0.588 |
ELM | 0.623 |
MIMO | 0.682 |
DL-CMA | 0.418 |
Some systems use channel compensation to fix signal problems. This keeps images clear, even when things are moving. These improvements help LCD screens show sharp visuals in busy settings.
Monochrome drivers are simpler and use less power. They control fewer pixels than color TFT drivers. Color TFT drivers manage millions of sub-pixels, each with its own transistor. This allows bright colors and high detail but uses more energy. New drivers now use AI to improve color and save power. This makes them great for phones and medical tools.
Chip-on-glass (COG) technology puts the driver on the LCD glass itself. This design removes extra parts, saving space and making it stronger. COG also sends signals better, keeping performance steady over time. Reviews show its reliability, with FSC LCD reaching a luminance efficiency of 5.13 cd/W. This is much better than older designs.
LCD Model | Luminance (cd/m2) | Power (W/m2) | Luminance Efficiency (LE) (cd/W) |
SHARP 60" LCD TV | 450 | 230 | 1.95 |
FSC LCD | 1,050 | 204 | 5.13 |
COG is now a top choice for small and energy-saving devices.

Backlighting helps LCD screens light up so you can see them. Without it, the screen stays dark because liquid crystals don’t make light. The backlight shines through the screen, making images and text clear indoors or outdoors.
Backlighting affects how well you can see an LCD screen. Devices like phones, medical monitors, and factory screens need backlighting for clear views. Brightness, measured in nits or candela per square meter (cd/m²), changes based on the device. For example, home devices need 200–400 nits, while military screens may need up to 1500 nits for sunlight visibility.
Parameter | Home Appliance Devices | Industrial Devices | Military and Marine Devices | Medical Devices |
Brightness (Nits) | 200–400 | 400–800 | 800–1500 | 500–1000 |
Luminance (cd/m²) | 200–400 | 400–800 | 800–1500 | 500–1000 |
When picking an LCD, think about the brightness you need. Higher brightness works better in bright places like outdoors or sunny rooms.
Edge-lit LEDs are common for LCD backlighting. They use LEDs on the screen’s edges to spread light with a diffuser and brightness-boosting films (BEFs). These films make the light stronger and more focused. Dual Brightness Enhancement Films (DBEFs) improve brightness even more than regular BEFs.
Technology/Film Type | Description |
Edge-lit Displays | Use a diffuser and crossed brightness films (xBEFs) to guide light. |
Brightness Enhancement Film (BEF) | Boosts light strength and narrows the viewing angle. |
Dual Brightness Enhancement Film (DBEF) | Offers higher brightness than standard BEFs. |
Light Guide Plate (LGP) | Spreads light evenly across the screen. |
These technologies save energy by focusing light better. This means less power is needed for the same brightness. Edge-lit LEDs and BEFs are great for devices where battery life matters.
Even backlighting makes the screen look smooth without bright or dark spots. This is crucial for tasks like medical imaging, where uneven light can cause mistakes. Manufacturers test screens for light consistency. For instance, the CG247X model has a medium variation of 5.1%, while the U2415b model has a higher variation of 8.1%.
Display Model | Medium Luminance Variation | High Luminance Variation |
CG247X | 5.1% | 3.5% |
U2415b | 8.1% | 8.5% |
Choose screens with low luminance variation for even lighting. This is especially important for professional or industrial uses.
Touchscreens are common in today’s LCD screens, but they work differently. The two main types—resistive and capacitive—have unique strengths.
Resistive screens need pressure to detect touch. They work with gloves, styluses, or in wet conditions. Capacitive screens sense the electricity in your skin. They are very sensitive and allow gestures like swiping or pinching. But they don’t work well in wet places or with gloves.
Here’s a simple comparison:
Feature | Capacitive Screen | Resistive Screen |
Touch Sensitivity | Very sensitive; allows gestures. | Needs pressure; no gestures. |
Works in Wet Places | No; struggles in wet conditions. | Yes; works fine. |
Cost | More expensive. | Cheaper option. |
Think about where you’ll use the screen before choosing. Capacitive screens are great for phones and tablets. Resistive screens are better for factories or medical tools.
Bezels and protective layers help LCD screens last longer and work better. Protective films, like optically clear adhesives (OCAs), improve how the screen looks by cutting down reflections. They also make colors sharper and easier to see in bright light.
Benefits of protective films include:
l Keep screen quality high by reducing light reflection.
l Stay strong over time without turning white.
l Block dirt by sealing gaps between screen layers.
Bezels give the screen extra support. They protect it from damage caused by drops or weather. OCAs also allow thinner bezels, giving more screen space without losing strength.
LCD screens can be customized for different jobs. For example, home devices use LCDs because they cost less and don’t burn out easily. Factories like them for their long life and low cost. In hospitals, special LCDs can match or even beat OLEDs for showing clear, detailed images.
Here’s a comparison of LCD and OLED benefits:
Use Case | LCD Benefits | OLED Benefits |
Home Devices | Low cost, long life, no burn-in issues | N/A |
Factory Equipment | Durable and affordable | N/A |
Military | N/A | Fast, clear images, wide viewing angles |
Marine | N/A | High contrast for better visibility |
Medical | Special LCDs rival OLEDs for clarity | N/A |
Customizing LCDs makes them useful and reliable for many industries.
LCD Displays show how amazing modern technology can be. Every part, like the LCD glass and backlight, works together to create clear and dependable images. These displays are built to last, save energy, and work well in many industries.
Here’s a table showing how LCD Displays perform:
Parameter | LCD |
Contrast Ratio | Usually between 1000:1 and 5000:1 |
Color Gamut | Wide, but smaller than OLED |
Viewing Angle | Colors fade at sharp angles |
Response Time | Ranges from 1ms to 5ms |
Lifespan | Lasts over 100,000 hours |
Risk of Burn-In | No risk |
Brightness | Very bright with LED backlights |
Energy Efficiency | Saves power with bright or white screens |
Cost | Cheaper than other display types |
LCD Displays have changed how we use screens today. They replaced bulky CRTs with thinner, lighter, and more energy-saving options. From TVs to phones and car systems, LCDs are now a big part of our daily lives.
LCDs use a backlight to light up pixels. OLEDs make their own light for each pixel. LCDs cost less and last longer. OLEDs show better contrast and darker blacks. Pick LCDs for saving money and durability. Choose OLEDs for top-quality visuals.
LCDs can’t make their own light. Backlights shine through to show images. Without backlights, the screen stays dark. They help you see the screen in all lighting, even outside.
LCDs use LED backlights and special films to save energy. These focus light better, cutting power use. Monochrome LCDs use even less energy, great for calculators and medical tools.
Yes, LCDs are tested for tough conditions. Tests check if they work in heat or cold. Sudden temperature changes are also tested. This makes them good for outdoor and industrial use.
Yes, LCDs can be made for specific jobs. Protective layers and touchscreens make them stronger. Brightness and resolution can be adjusted. Medical LCDs focus on clarity, while industrial ones are built to last and save energy.